Feel free to comment and subscribe to be notified when a new article is published.
* Article based on a Gartner report by Bob Gill and David Smith
Edge computing places content, data and processing closer to the applications, things and users that consume and interact with them. Edge computing complements legacy clouds. Technology leaders must be ready for this new edge revolution.
Some interesting aspects of edge computing are:
According to Gartner*, “By 2022, more than 50% of enterprise-generated data will be created and processed outside the data centre or cloud. By 2020, 80% of asset-intensive industry CIOs will be responsible for operational technology (OT) data, and will embrace IT/OT integration as a strategic imperative.”
In this article, we will explore…
What edge computing is, and which technologies help shape it
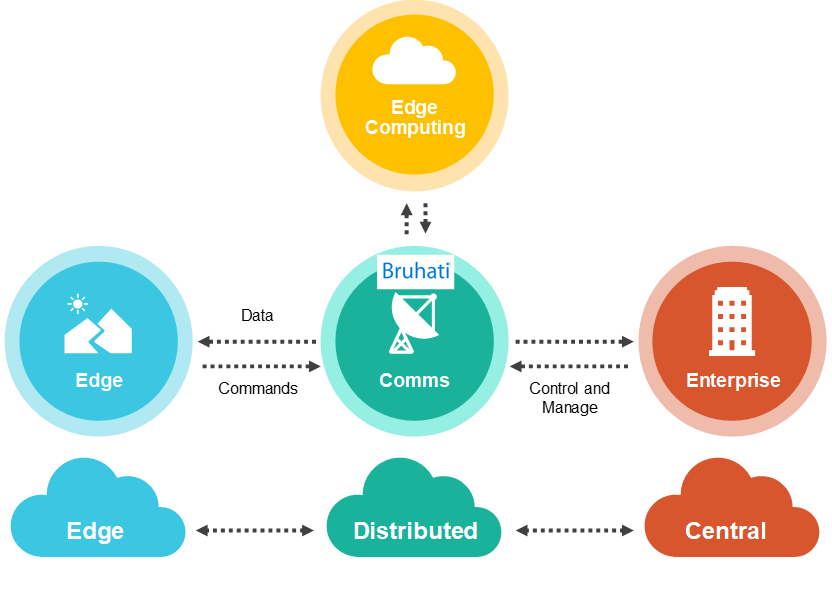
Gartner* define edge computing as composed by 3 layers:
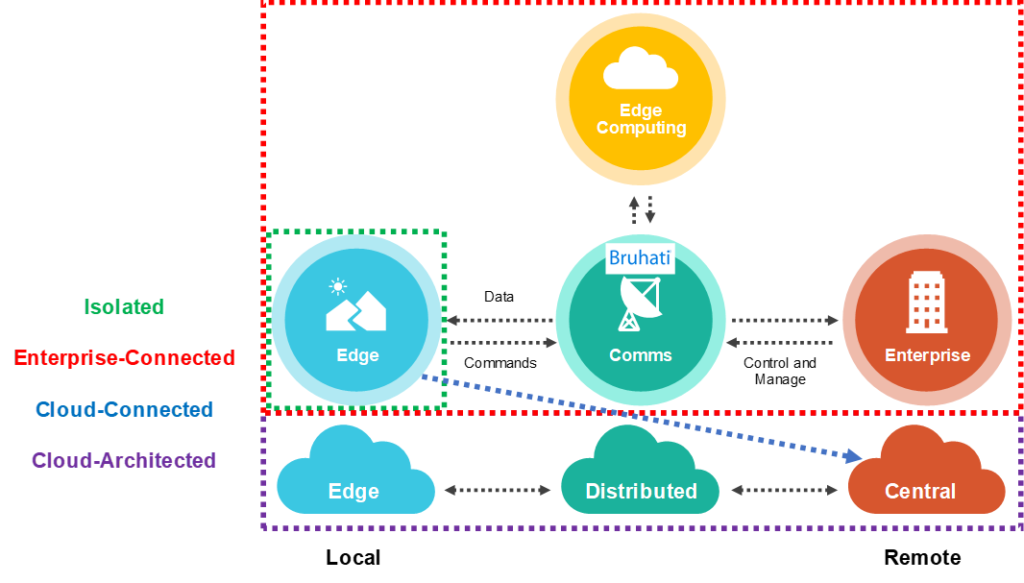
How edge computing can be beneficial
What the future holds for the edge and the cloud
With cloud computing becoming more and more common, the IT environments of many organizations include public and some private cloud, along with conventional IT systems. It is a widely held belief amongst organizations that hybrid scenarios can be used to help resolve issues that environments with a variety of different IT systems face. Gartner noted the following patterns at their cloud Hype Cycle:
Some limiting factors that affect implementation are; the speed of light, the cost of transporting huge amounts of data back and forth and the cost of cloud data ingress/egress. These have led even organizations with large-scale cloud operations to conclude that centralized cloud and distributed edge are both equally vital.
Gartner* estimates that IoT endpoints “will reach an installed base of 25.1 billion units by 2021”. Edge computing has garnered a lot of attention because of a demand for IoT systems to provide disconnected or distributed functions to the IoT world. Edge computing an effect on almost every aspect of the IT landscape; with Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) leading the trend”.
With digital transformation now happening all around the world — you must be ready to adapt. Our Partner Bruhati can help you to define your cloud strategy. For more information and a FREE consultation please visit www.bruhati.com or write at sales@bruhati.com.
Feel free to comment and subscribe to be notified when a new article is published.
* Article based on a Gartner report by Bob Gill and David Smith